Species tool: Version 1 (script)¶
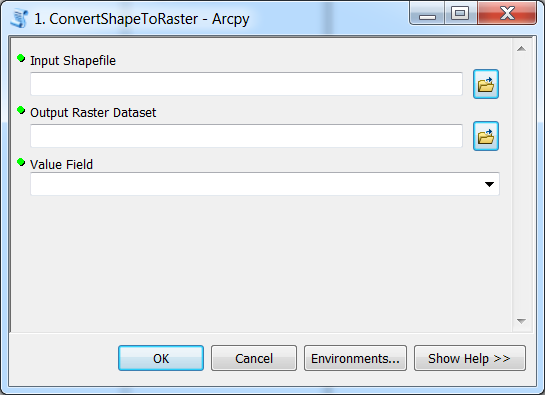
At this point we have created a nice interface for our Python tool in ArcGIS:
Next we need to write the functionality for our tool. The first version of our tool will simply convert Shapefiles into raster using the polygon to raster conversion -tool and print out a customized message for the user.
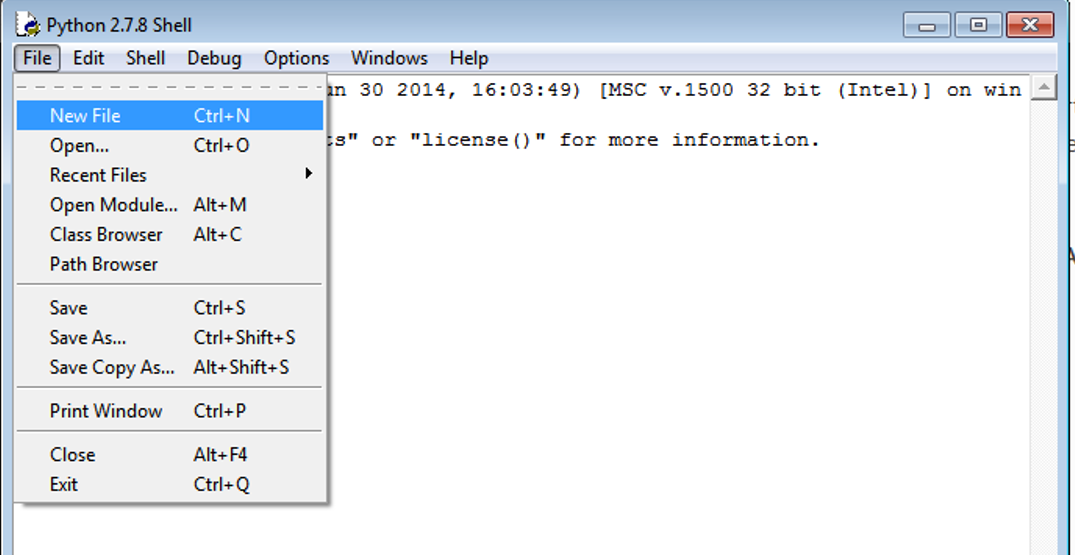
First, we need start the ArcGIS IDLE (if it is not open already) from All Programs –> ArcGIS:
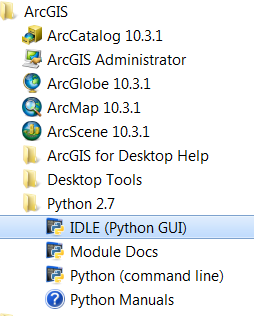
Create a new script called Arcpy_1_SimplePoly2Raster.py in IDLE (File –> New File) and save it to your computer:
Let’s start writing the functionality of our tool to the script that we just created.
Importing arcpy¶
First thing to do is to import the arcpy module:
# Import neede modules
import arcpy
import os
Note
Notice that arcpy can only be imported with Python interpreter that comes with ArcGIS. If you try to import it e.g. in Spyder, you will receive an error ImportError: No module named 'arcpy'.
Well...actually there is a way to import arcpy from other places as well and also import it into Spyder but we will not cover this during our course.
Getting parameters from the toolbox¶
Before we can do anything with our tool and our nice interface for it, we need to get those parameters into our script. This can be done by using arcpy’s function called .GetParameterAsText() where the index
value of the parameter is passed to the function (where number 0 is the first parameter). ArcGIS has a good documentation that should be used for searching the information about how different functions are used.
Let’s import the first parameters from the graphical interface into our Python script using GetParameterAsText() -function:
Also, let’s add a line of code which enables arcpy to owerwrite existing files: arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True.
Full script so far should look like this:
# Import neede modules
import arcpy
import os
# Enable Arcpy to overwrite existing files
arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 1. Get parameters from the toolbox using 'GetParametersAsText' method
# --> check ArcGIS help for info how to use methods
# Method info: http://resources.arcgis.com/en/help/main/10.2/index.html#//018v00000047000000
#---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
input_shp = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)
output_raster = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(1)
value_attribute = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(2)
Now we have a link between the user interface and the script. Next, let’s call the required tool for converting input shapefile into raster using the given parameters:
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# 2. Convert input Shapefile into a Raster Dataset using 'PolygonToRaster_conversion' method
# Method info: http://resources.arcgis.com/en/help/main/10.2/index.html#//001200000030000000
#--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
arcpy.PolygonToRaster_conversion(in_features=input_shp, value_field=value_attribute, out_rasterdataset=output_raster)
Info messages¶
It is possible to “print” messages to the user-interface while the tool is running. The regular print() -function won’t do in this case and
we need to use AddMessage() -function (see help) to send
any kind of messages to the user-interface of our tool.
Let’s add a message at the end of our script:
#Print that the process was finished successfully
message_text = "\n\nProcess was a great success! \nOutput generated: " + output_raster + "\n\n"
arcpy.AddMessage(message_text)
Save the full script as Arcpy_1_SimplePoly2Raster.py.
Now, we have a script that we can use from our Toolbox in ArcGIS! Let’s next see how it can be used.